Blockchain, Web3 and The Future of the Digital Economy
Are you searching for what is Web3 technology and why it matters? Congratulations, you are in the right place. Let’s discover together this emerging idea that could upgrade the way we interact and are involved in online activities.
Web3 is a blockchain-based technology incorporated with decentralization and smart contracts, and it is a significant transition that provides a secure, user-friendly platform that allows individuals to have ownership and identity of their digital assets to enhance users’ economic growth and security in the online world.
Get ready to explore in this blog post how Web3 helps users to get back their power of ownership and identity in a secure environment. You can also learn the reasons why Web3 matters in developing modern economic models and boosting the internet. Imagine how promising future plans are to modify our digital interactions.
Understanding the Power of Web3 Technology
Web3 technology is the transformation from a centralized to a decentralized internet, empowering users with significant control over their data, digital identity, and digital assets through a blockchain-based network that, in addition, provides secure and transparent data management.
The Web3 ecosystem consists of integrated applications and technologies; in particular, it comprises decentralized applications (dApps), decentralized finance (DeFi), and NFTs (non-fungible tokens). Moreover, it enables the ownership and creation of exclusive digital assets.
Foundational Principles of Web 3 Technology
Let’s discover the key pillars of driving Web3 technology. A decentralized, secure, and user-empowered digital future awaits you!
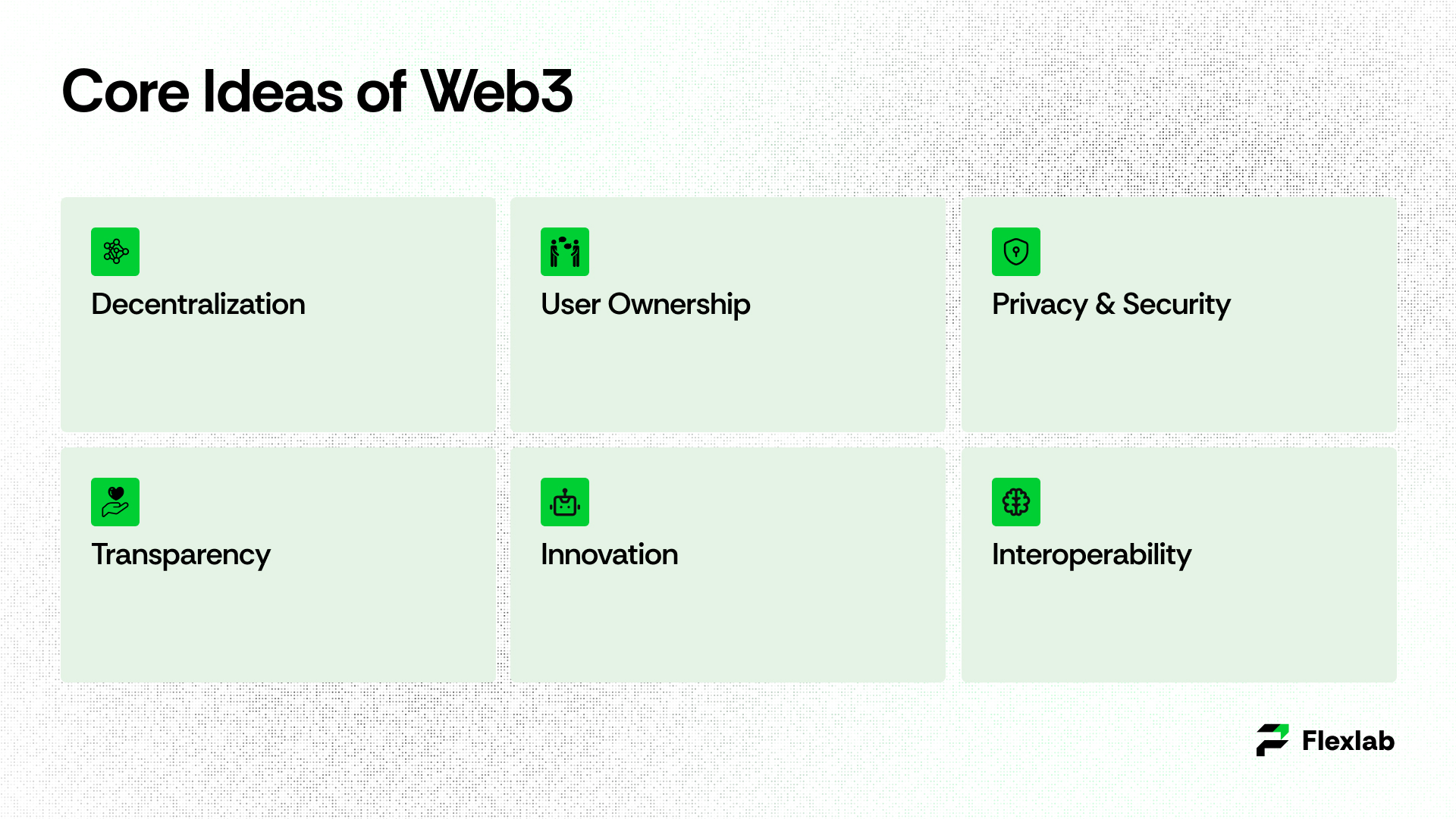
- Decentralization: Distributed power across the blockchain network.
- User ownership: Users own their data, identity, and digital assets.
- Privacy and security: Users control the shared information, protected by cryptographic technology.
- Transparency: Blockchain verifies all the transactions and processes to build trust and accountability.
- Innovation: Users are rewarded for contributing to the Web3 ecosystem; therefore, it promotes participation and, moreover, drives development.
- Interoperability: It enables different decentralized apps, blockchain networks, and other services to work together, providing a smooth and innovative user experience.
Key Features of Web 3
The distinct features of Web3 make it unique and compelling, working together to develop a strong and user-centric Web3 ecosystem.
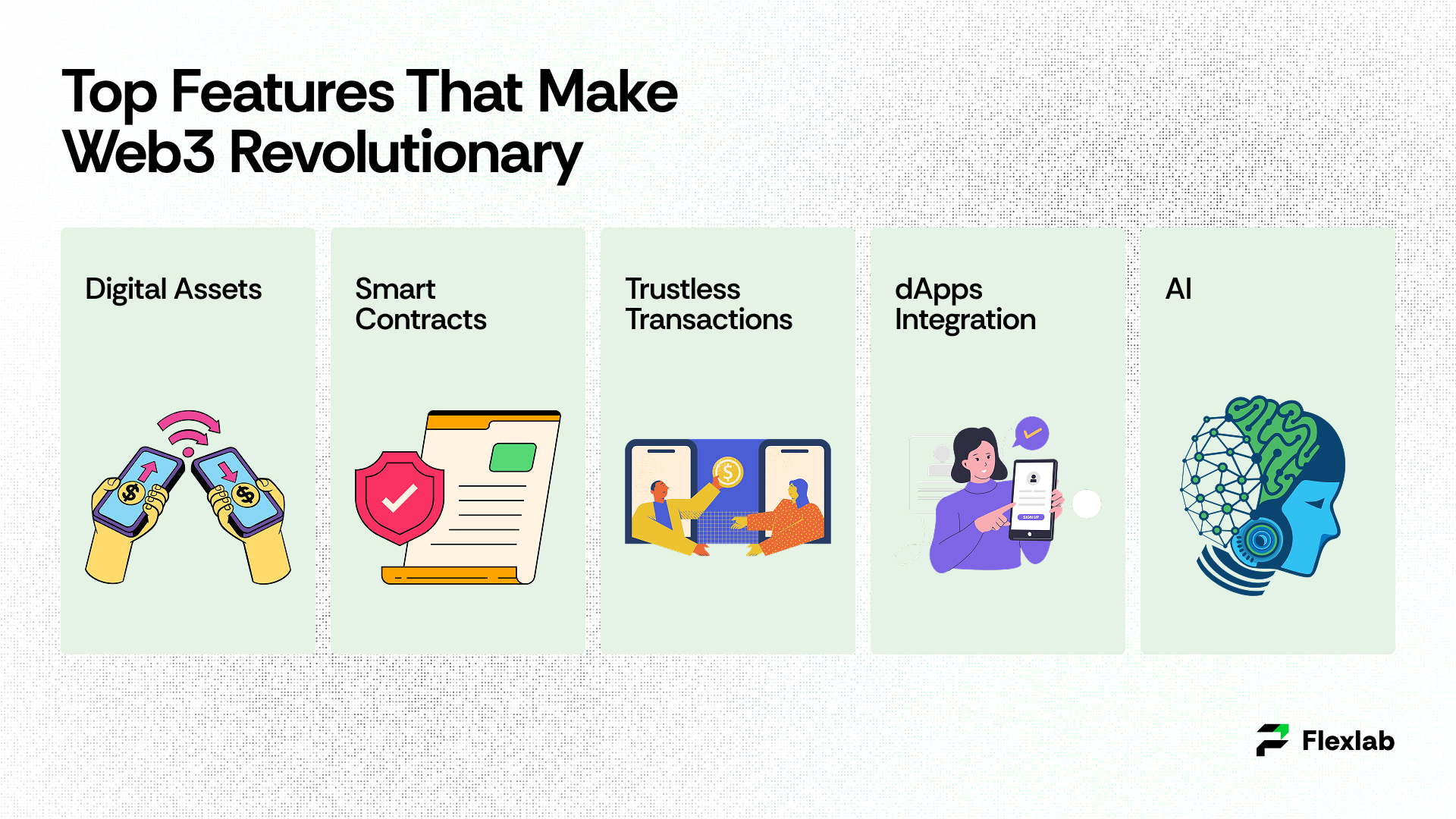
1. Digital Assets
Digital assets comprise currencies, digital art, and digital content, such as NFTs (non-fungible tokens) or cryptocurrencies, which are, in fact, in the direct ownership of the user and are recorded on a secure blockchain. Furthermore, this system facilitates and empowers startups since users can, therefore, monetize their digital content by themselves.
2. Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-imposed agreements stored on the blockchain. In addition, when predetermined conditions are completed, they become automatically active. As a result, they remove the need for middlemen and ensure openness, security, and trust. Consequently, these contracts enable rapid, cost-graduated transactions as well as decentralized applications (dApps).
3. Trustlessness
Web3 users can enjoy transparency and consistency; moreover, they benefit from the absence of intermediary interruption for transaction verification. In addition, it enables different decentralized integration apps (dApps), blockchain networks, and other services to work together, thereby providing a smooth and innovative user experience.
4.DApps Integration
Decentralized applications (dApps) run on blockchain networks and offer services without relying on centralized control. Their integration allows users to interact directly with smart contracts to ensure security. Dapps can cover various fields such as finance, games, social media, and supply chain. Seamless dapp integration increases the user experience and promotes a more open, innovative Web3 ecosystem.
5. New Artificial Intelligence Technology
Machines can interpret data intelligently with the advent of the “semantic web,” a network where machines can, therefore, understand, analyze, and process data more effectively. Moreover, the integration of new artificial intelligence technology, advanced AI, and machine learning helps develop an efficient online experience with more personalized and useful content. In addition, AI helps in fraud detection; it can also enhance smart contracts and, consequently, manage decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs).
4. Why Does Web 3 Matter?
Web 3 matters due to its revolutionary offers, such as:
- Decentralized autonomy: Users participate in the system without centralized control.
- Real Digital Ownership: Property and identity are directly related to individuals.
- Data privacy and security: Blockchain reduces fraud and risk of abuse.
- Freedom from central authority: No single institution determines rules or access.
- Innovative income streams: Cryptographic tokens and NFTs are opening up fresh opportunities for businesses to generate revenue.
- Transparency and trust: Open protocols make the transaction confirmed and reliable.
What Technologies Support Web3?
Web3 is a revolutionary technology that enables users to own and interact with the internet. Let’s explore the key building blocks that support the Web3 ecosystem:
1. Blockchain
It is a decentralized distributed ledger that records transactions across multiple computers, known as nodes, ensuring transparency and security. Such that:
- Ethereum: The most authoritative platform to build Web3 apps.
- Polygon: Ethereum scaling solution for faster and lower-cost transactions.
- Solana: With an output of 65000 transactions per second at low fees, it is ideal for multiplayer and real-time games.
In short, Web3 is a blockchain-based technology that supports decentralization.
2. Smart Contracts- Zero Intermediary Interaction
Self-regulating autonomous programmes stored on the blockchain run when suitable conditions are available. Curtail the intermediaries like brokers, lawyers, and banks.
Real-world cases of smart contracts are;
- Uniswap is a decentralized finance (DeFi) protocol used for decentralized trading.
- NFTs (Non-fungible tokens) enable autonomous royalty transactions.
- The DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) voting system utilizes tokens to make decisions together.
Simply, a smart contract is a program that autonomously executes transactions and agreements on the blockchain.

3. Cryptocurrencies and Tokens – The Web3 Currency
Digital currencies such as Bitcoin, ETH, etc., besides digital assets such as utility tokens, facilitate digital transactions and fuel decentralized ecosystems. It gives powers to the Web3 economic model by providing payment for services, rewarding users for participation, and enabling governance. In short, digital tokens are the oxygen of the Web3 economy.
4. Cloud Storage – A Decentralized Approach
Decentralized cloud storage gives power to users over companies and provides a secure self-sovereign identity system based on blockchain technology. Users then have control over their personal information and data.
There are some examples of cloud storage:
- ENS (Ethereum Name Service): It is a decentralized domain name service (DNS) that allows users to register and manage their unique domain names like “username.eth” on the Ethereum blockchain.
- Civic: It is a decentralized identity verification platform based on blockchain technology; therefore, it allows users to keep a check on and, moreover, securely manage their personal information with respect to identity and data.
- Decentralized cloud storage serves the purpose of giving power to users while making data in Web3 accessible, secure, and transparent.
5. Decentralized Identity (DID) – Users’ Digital Passport
(DID) is a decentralized identity that gives users control over their personal information and interactions online. In addition, this blockchain-based technology allows users to manage and verify their identity safely; as a result, they do not need to involve or rely on other authorities.
Examples of DID are:
- MakerDAO: It is a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) that operates on the Ethereum Blockchain and is known for the stablecoin DAI.
- AAVE DAO: A decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) controls the Aave Protocol, a lending platform on the Ethereum Blockchain. In turn, this enables users to borrow and lend cryptocurrency.
Get ready to unlock a secure digital future for transactions and interactions online by the owner of your own digital identity without relying on technical giants.
6. Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) – Empowered Blockchain Ecosystem
It is a blockchain-based outfit run by the members and operated autonomously; at the same time, it ensures transparent control by the users.
Examples include:
- MakerDAO: A decentralized loan platform managing StableCoin DAI.
- AAVE DAO: A decentralized loan platform that allows users to borrow and lend Cryptocurrency.DAO’s return decision-making into users’ hands.
7. Web3 Browsers – Gateways to the Future
It allows users to connect to decentralized applications (dApps) and blockchain-based services; as a result, it ensures openness and security while supporting lightweight wallet administration, as well as interacting with and detecting dApps.
Example:
- Brave browser: This is a privacy-centred browser with the underlying crypto wallet.
- Opera Web 3 browsers: Spontaneous interaction with decentralized applications and support different cryptocurrencies.
Web3 browsers are the entrance to a world where freedom meets innovation.
8. Oracles Bridge the Gap – Unlocking Blockchain Potential
These are services that provide data from the real world to smart contracts; likewise, blockchain relies on them to access external information.
Example:
- Chainlink: Smart contracts provide a safe and reliable data feed.
- Band protocol: Provides sharp and secure data integration on several blockchain ecosystems.
Oracles connect dots between blockchain and the real world.
9. Layer-2 – Speeding Up Web3 with Lower Cost
It is a protocol based on blockchain that increases speed and controls transaction costs; moreover, it enhances users’ work experience and encourages the adoption of Web3 applications.
Examples are:
- Polygon: A layer 2 scaling system that provides fast and low-cost transactions. Additionally, it enhances the overall user experience by reducing network congestion.
- Optimism: An optimism rollup solution for Ethereum that enables fast and cheaper transactions. Furthermore, it helps scale Ethereum without compromising security.
- Mediator: A scaling system that uses optimized rollups to increase scalability and reduce costs. As a result, it supports broader adoption of Web3 applications.
10. Interoperability Protocols – The Key to Web3 Ecosystem
These are technologies that enable various blockchain platforms, networks, and decentralized applications to share, communicate, and interact initially. In addition, interoperability protocols play a crucial role in building a user-friendly, efficient, and integrated Web3 ecosystem.
Examples are:
- Polkadot: Develop interoperability between multiple blockchain networks to share assets and data.
- Cosmos: These are independent, scalable blockchain interoperability networks.
- Interoperability protocols enable spontaneous interaction and unlock new opportunities for an associated universe.
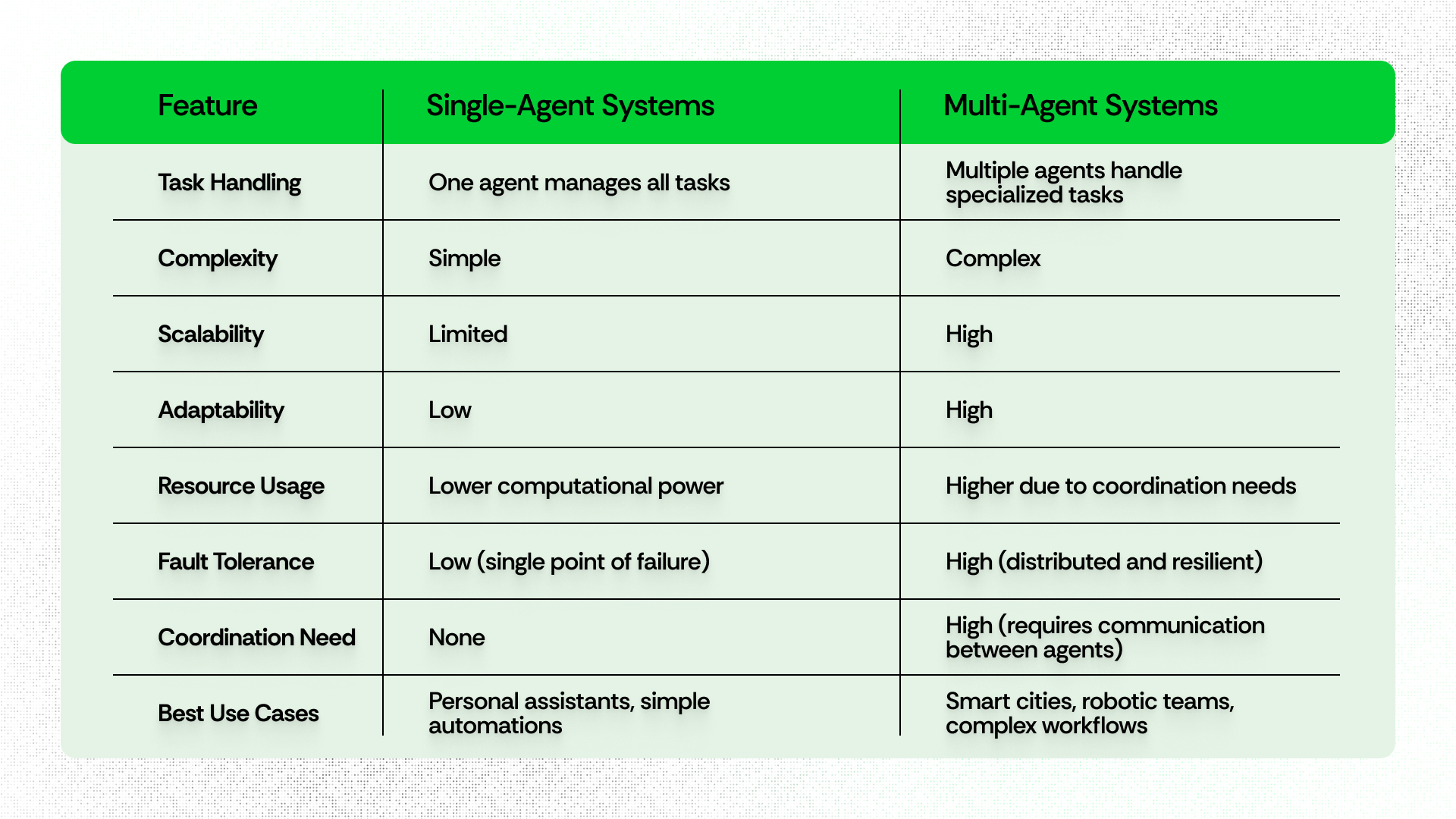
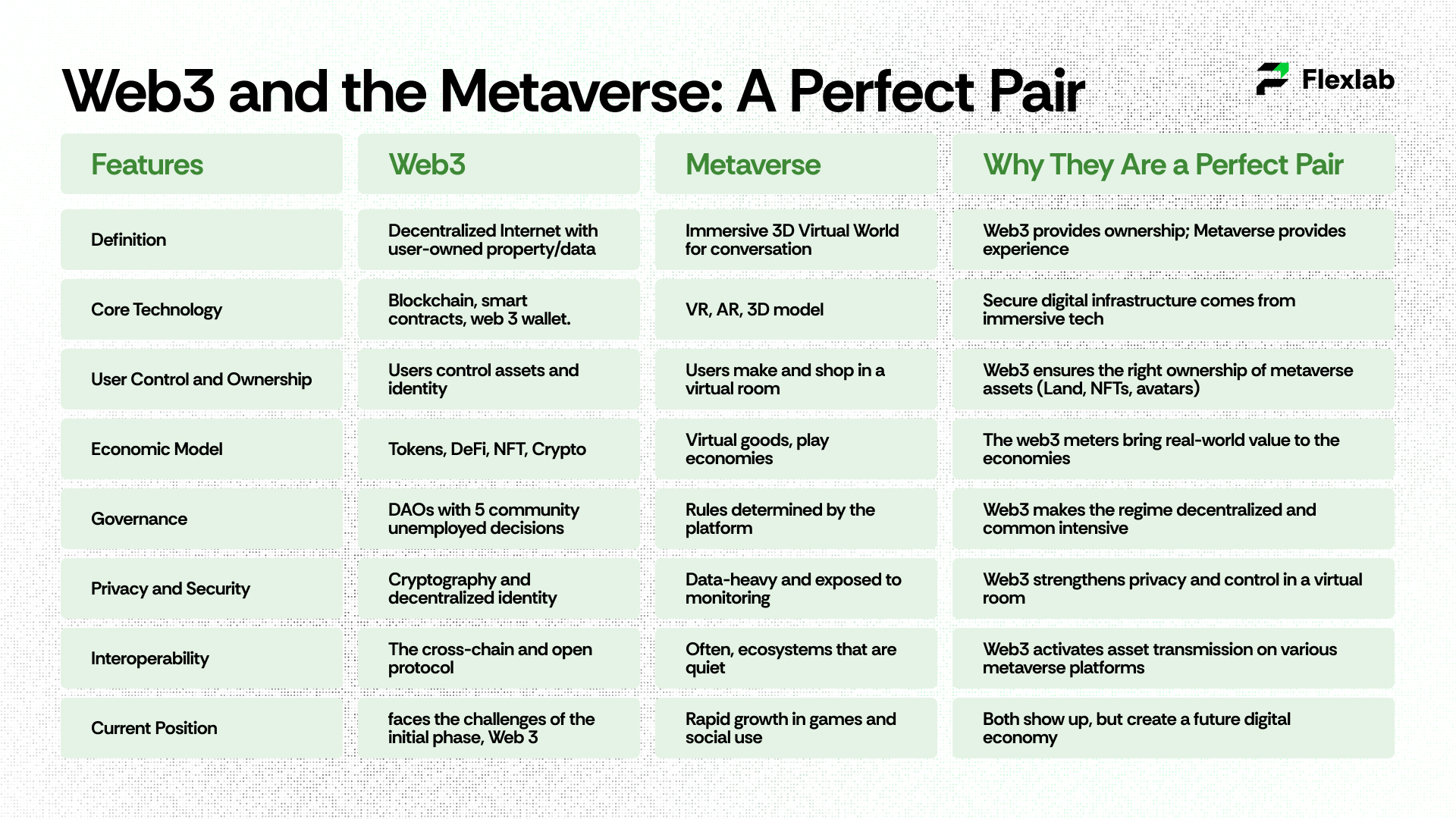
Web2 vs. Web3: A Detailed Comparison
What makes Web3 innovative? Let’s take a deeper dive.
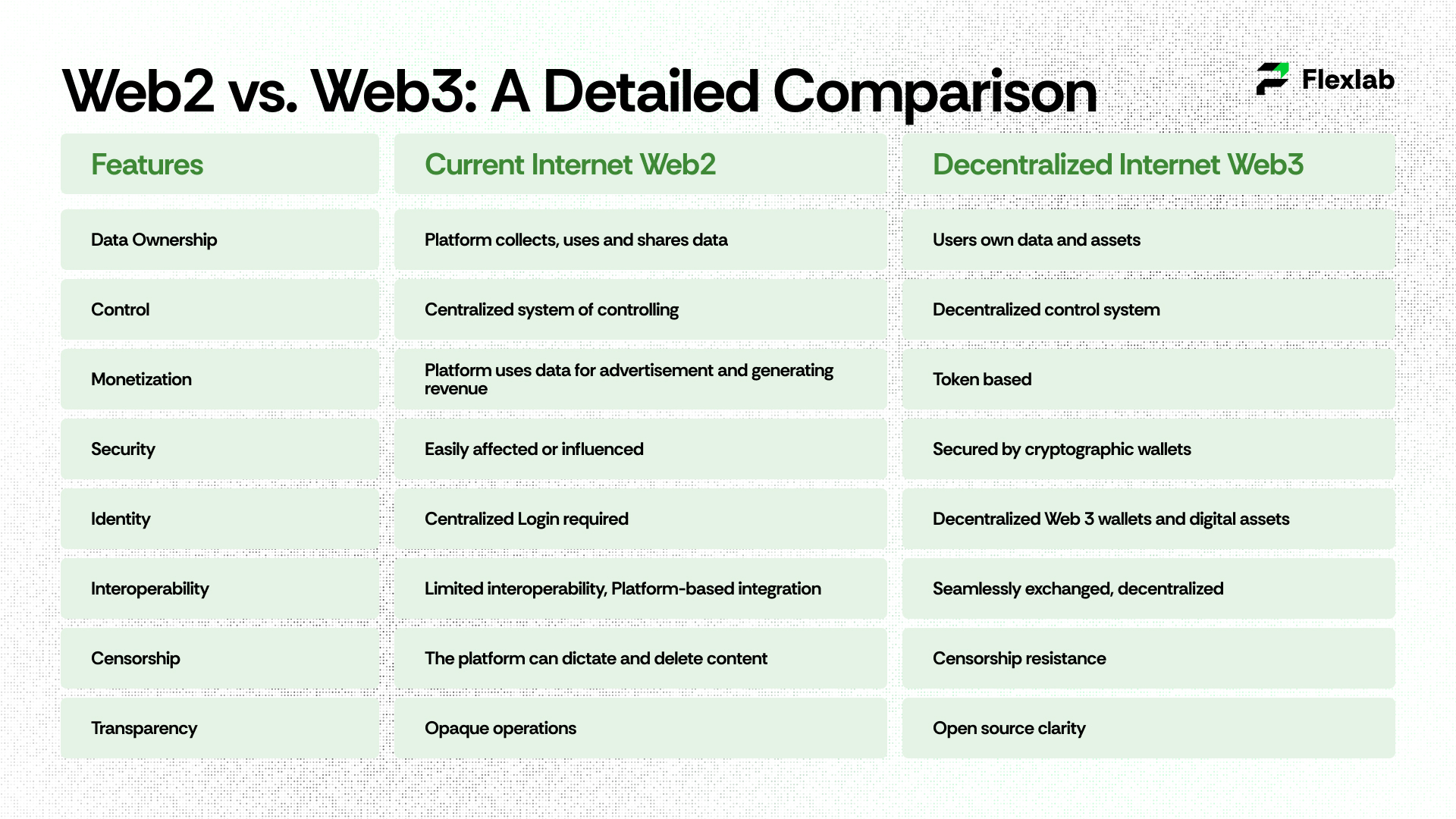
Web3 empowers users by shifting control from corporations to individuals; in fact, it signals a fundamental transformation in the digital world.
Web3 Reality Check: Challenges and Limitations
It is a revolutionary idea for the upcoming generation of the Internet, which promises to provide a secure Internet and reopen the digital world. From its inception, Web3 faces several challenges and limitations that must be addressed and resolved carefully to enjoy the exciting journey of Web3 that is not so far.
Let’s take a closer look at all the challenges and limitations that Web3 is expected to face.
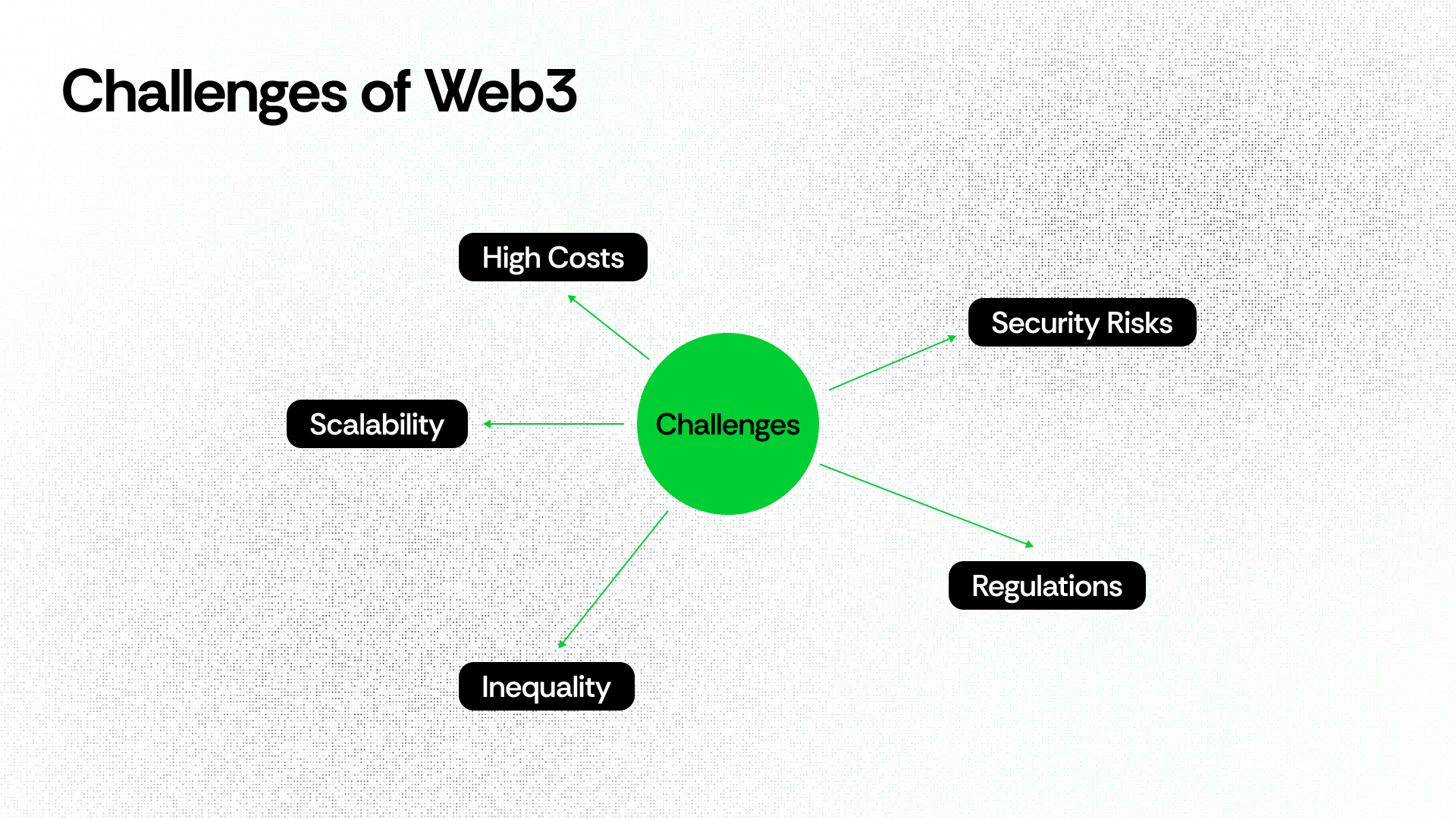
As we are aware, Web3 is a blockchain-based network that gives priority to security and decentralization over speed. However, with the increase in demand, its performance is affected; consequently, it slows down, and the cost increases notably.
Blockchain transactions can be super expensive. Sometimes, the fee is higher than what we’re sending! When multiple people use the network at the same time, it gets overloaded and fees shoot. This creates an issue for people with limited budgets.
Although blockchain technology is generally secure, other tools built around it, including smart contracts, crypto wallets, and decentralized exchanges, can nevertheless face vulnerabilities like hacking and unethical use because of these issues. Many people lose millions of dollars. There isn’t any user support system that recovers these losses. Therefore, effective security measures and user awareness are crucial to eliminate or reduce the risks.
All over the world, governing bodies are trying to regulate decentralized currencies such as Crypto, DeFi, and Web3. Some countries adopt innovation while others ban or impose restrictions on it. Rules and regulations are inconsistent, which creates uncertainty among investors and businesses and ultimately affects growth. The imposition of too many rules kills innovation; in contrast, fewer rules could increase the chances of scams and assaults.
Web3 wants to build a fairer internet; however, the lack of knowledge and unequal access to technology are not supportive. Consequently, Web3 could benefit only those who have a good understanding of technology and can use it effectively.
Web3 Adoption Strategies for Businesses
Educate and Upskill Teams: The first step is building internal knowledge. As a result, companies need to train employees about the rise of Web3 and how it differs from Web2, along with the opportunities it creates. Furthermore, partnering with a dependable Web3 developer will help teams gain hands-on experience.
Start with a Small Pilot Project. Rather than jumping straight into everything, companies should start with a few pilot Web3 applications, such as trial runs for Web3 wallet integration for digital payments or loyalty programs, with minimal pre-investment.
Integrate and Bring Blockchain into Present Operations
Companies can streamline the procedures by bringing blockchain into their systems. It can range from supply-chain to financial reporting, cutting through incompetence in preparation for widespread adoption, where central-bank digital currency transactions will come later.
- Exploitation: Tokenization lets companies create digital assets representing value in the real world. In addition, from loyalty to part-time ownership of assets, this approach could transform customer engagement.
- Collaborate with web3 partners: A Web3 expert develops strategic collaboration implementation with ecosystem partners or other developers. The partnership provides access to networks in areas such as the Metaverse or IP network (Internet Protocol network), where adoption increases.
- Priority to security and compliance: When new models emerge, Web3 challenges, such as security risks and vague rules, require attention. Consequently, companies should collaborate with legal and cybersecurity experts to ensure compliance and safeguard their users.
Opportunities Web3 Offers to Businesses
- Direct User Engagement: Token rewards and personalized experiences strengthen customer relations, fostering loyalty and direct engagement.
- NFTs & Tokens: New monetization instruments such as NFTs, tokens, and metaverse services unlock a new mode of income.
- Global Reach: Services inherently become available to any user worldwide who holds a Web3 wallet; as a result, decentralized platforms extend their reach to everyone.
- Web3 Partnership: Customers gain greater control over their digital identity and better transparency.
- AI + Web3 Synergy: Businesses that embrace the growth of Web3 before competition will be the ones to carve out the market.
Use Cases and Real-world Applications of Web3
1. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi ends the requirement for conventional middlemen, such as banks and brokers. Instead, it executes transactions for loans, strikes, and trades on decentralized protocols operated by smart contracts. Only with a Web3 wallet can a user avail financial services across the globe at any time without any spatial or credit history burdens. Thus, DeFi opens new opportunities for companies to transact payments and financings and also to border transition alternatives that stand in the way of the existing central bank digital currency systems.
2. Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
NFTs do much more than just digital art. From the brands’ perspective, things like limited products, membership seats, and interactive fan engagement are some of the new use cases. Moreover, an NFT can act as a certificate of authenticity or a digital collectible connected to real-world experiences. As a result, this use case becomes central to marketing strategies. It propels companies to evolve through a very user-driven campaign, whereas Web 2 platforms enable creating brand loyalty in ways that Web 2 cannot.
3. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
Instead of corporate hierarchies, the DAO runs as a society governed by token holders. Members cast their votes on proposals, allocate resources, and earn parts in the outcomes. In this manner, a DAO presents alternate models of funding and management to start-ups. Traditional firms could also institute transparency systems and processes of employee participation inspired by DAOs, yet this is where we see the evolution of the Web3 regime versus traditional frameworks.
4. The Supply Chain Transparency
Each supply chain step is recorded and verified in an irreversible manner using the blockchain technique. This helps in establishing the authenticity of products, avoiding fraud, and increasing accountability. Making the supply chain transparent, from agriculture to luxury goods, becomes the greatest Web3 application, instilling equal trust within customers and regulators while addressing sustainability concerns.
5. Gaming and Play-to-Earn model
The gaming industry accelerates Web3 development. Those who play the Play-to-Earn model allow tokens or businesses to serve as digital assets that carry fair value. In conjunction with the metaverse, players can use NFTs for avatars, leather, and in-game activities, thus generating a rich virtual economy in the process. Brand experiences created by companies also come into this site, from locations outside of games within this virtual environment.
6. Digital Recognition and Privacy of Data
Traditional systems depend on centralized databases that are often considered unsafe for fractures. In contrast, Web3 introduces self-confidential identity, where users control their credentials through the Web3 wallet. As a result, this changes the ownership relationship of data from companies to individuals and, furthermore, reduces security risk by increasing confidence. For companies, this, in turn, implies using decentralized identification frameworks, ensuring strong compliance, and enabling secure customer interaction.
7. Material Creation and Social Media
On the Web2 platforms, creators often suffer because the revenue is based so heavily on ads and algorithms. In contrast, in the Web3 model, applications reward creators directly through tokens, NFTs, or decentralized revenue-sharing methods. This paves the way for a more beneficial ecosystem where most value is in the hands of users and not the platforms. For companies, this brings opportunities; in particular, it allows them to create direct collaborations with creators on a transparent basis.
8. Tokenized Real-World Assets
Tokenization offers everything for the digitization of physical assets, be they real estate and objects, or securities. The token parties, then, become much easier to trade, which was otherwise discouraged, therefore also opening up access to investors. Improvement in liquidity and transparency is what Tokening brings to the financial markets as one of the most promising Web3 applications, minimizing the gap between traditional systems and decentralized innovations on an Internet Protocol network.
Final Thoughts on Web3 Technology
Web3 applications are the next step in the development of the Internet; in fact, they transfer the power from centralized platforms to users. Moreover, with Web3 applications, Web3 wallets, and blockchain-based ecosystems, individuals and businesses receive real ownership of data, assets, and identity. Furthermore, from DeFi and NFTs to the metaverse and symbols, the possibilities are truly great. While the challenges with Web3, for instance, regulation and scalability, working with a reliable Web3 development company can help navigate these challenges. In the long term, Web3 means something because it creates a more transparent, safe, and user-driven digital economy.
How can Flexlab Support Web3 Application Requirements?
Are you ready to take your digital presence to new heights? If so, start building your Web3 app today with Flexlab and turn your dream into a reality to explore the limitless possibilities of Web3 applications and unlock your full potential.
Flexlab, a trusted partner in your revolutionary journey of Web3 development, offers powerful tools, expert guidance, and seamless integration with smart contracts, blockchain, and decentralized technologies. Whether you decide to launch a decentralized app, NFT marketplace, or any other next-generation Web3 project, Flexlab provides the expertise and support to accelerate your vision forward.
Reach out to our experienced team. Contact us to discuss your Web3 projects and explore the portfolio of your partner in Web3 innovation. Let’s collaborate to develop outstanding solutions that take your business to the next level.
Discover More:
Blockchain App Development: The Complete Guide for Businesses
AI vs Automation: Decoding the Differences for Business Success
What Are AI Agents? A Beginner’s Guide (2025)
[sc_fs_multi_faq headline-0=”h2″ question-0=”How does Web 3 work?” answer-0=”Web3 uses a decentralized protocol operated by blockchain and peer-to-peer networks. Unlike traditional systems, it removes the brokers and gives users direct control over the data and digital assets. With a web3 wallet, individuals can safely act without relying on centralized officers and transfer themselves. It enables secure and transparent transactions to promote a trustless domain. Individuals can directly interact with Web applications, encouraging innovations and community-driven growth. ” image-0=”” headline-1=”h2″ question-1=”Is Web 3 the future?” answer-1=”Yes. Web3 represents a change to decentralization, openness, and usage in the digital economy. Many technical companies and even governments are searching for Web3 applications, from blockchain solutions to a central bank digital currency model, which indicates it is the main part of the Internet of the future. This transition is expected to enhance innovation, improve security, and generate new economic opportunities.” image-1=”” headline-2=”h2″ question-2=”What is Web3 technology for dummies?” answer-2=”Think of Web3 as the next version of the Internet, where you own your data and digital identity. Instead of large companies controlling everything, you keep keys through blockchain and Web3 wallets. This allows you to send and receive digital currencies directly without banks or middlemen.Web3 technologies also enable transparent and secure interactions in the presence of smart contracts, developing trust and automating processes. With the help of Web3, users have more autonomous power to manage digital transactions according to their convenience. ” image-2=”” count=”3″ html=”true” css_class=””]